What is the Silk Road?
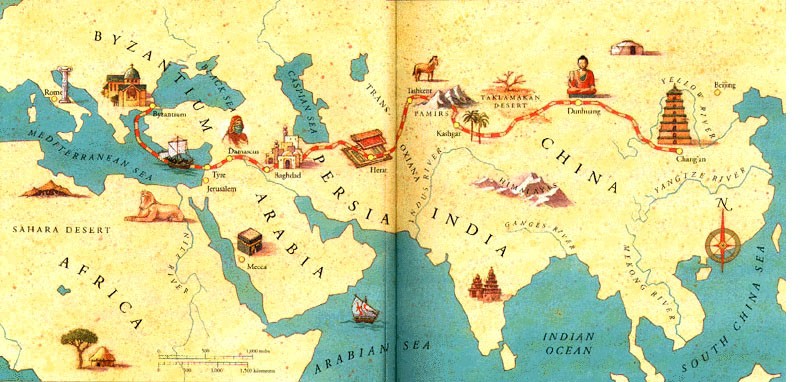
Silk Road
The Silk Road - the main trade route connecting Asia to Europe - was dotted with caravanserai hosting merchants and pilgrims. Caravanserais provided accommodation, security, food and amenities for travelers, their servants, merchandise and animals (usually camels). Merchants could stay at caravanserais, rest, refresh themselves and even trade with each other in a secure and relaxing environment.
Caravanserais often had a square or rectangular plan with a large wide portal and high walls. The courtyard was almost always open to the sky. The basic architecture of Persian caravanserais, like many other local structures, was determined by the tradition and style of the era it was built in. Architectural styles of caravanserai reflect local styles and the construction materials available in each geographical locality.
Guest rooms were built around the courtyard and the stables were located behind them with their doors in the corners of the yard. In the Safavid dynasty, the designs of caravanserais diversified and in addition to four iwan (vaulted hall) caravanserais, other forms such as circular, octagonal and desert caravanserais were introduced.
Caravanserai (caravansary, karvansara) is a compound word combining "caravan" (karavan) with "sara".
A caravan means a group of travelers and sara a home, place or building. Caravanserai is thus a place where the traveler can reside and rest from his or her journey.
History of Caravanserai
Remains of these early hotels and resting places are scattered along the roads and in the cities of Iran. Many caravanserai in Iran are considered to be both artistic and architectural masterpieces of their age.
The first caravanserais in Iran were built when the Achaemenid Empire (circa 550–330 BC) ruled Persia. Along with the development of road systems and the increase in the number of travelers and merchants during this time, these old roadside inns increased and flourished along the trade routes of the old Silk Road.
Shah Abbas I (1571-1629) is credited with building a network of caravanserai across Iran during the much later Safavid dynasty.
Commercial Caravanserais
Some of the commercial caravanserais within the cities were built as two-story buildings often located right next to the bazaars to facilitate the transfer of goods. Caravansaries often had a well or an abanbar in the middle of the courtyard or outside the building to provide travelers with much needed water. In examples of Persian Gulf caravanserais, abanbars were located outside the main walls of the structure, while in the central regions of Iran you can find abanbars, baths, the mill, shops, the bakery, the butchery and a place to pray inside the caravanserais.
Two examples are Dayr-e Gachin in the south of Tehran and Mahyar caravanserai on the Isfahan-Shiraz road. In many of the caravanserais built in the post-Safavid era , there was a fire-place where the travelers could light a fire. In the hot, desert regions, badgirs were built to cool and refresh the rooms. Badgirs were often built on the iwans, opposite the main portal, as at Zin-o din in Yazd and Jokar in the vicinity of Tabas. The remains of old caravanserais show that there would have been rooms for guards and officers to protect the travelers within.
The main construction materials of caravanserais in Iran were brick, stone and sometimes adobe. In the Safavid dynasty, caravanserais, like their contemporary religious structures, had architectural decorations such as brickwork, tile work, molding and masonry.
Decorations were often used on the outer façade of caravanserais, in the portal, iwans and arches. Robat Sharaf, Robat Chaheh, Mahyar and Gozar are some caravanserais with remarkable decorations.
In the Islamic period, the architecture of caravanserais reached its peak in design, style and variety. Many remarkable and beautiful examples of Islamic architecture are preserved all over Iran from the banks of the River Aras to the shores of the Persian Gulf. These beautiful buildings represent the artistic taste and skills of numerous architects, bricklayers and craftsmen who constructed these early way stations.
Today caravanserais have largely lost their old usage and popularity as places to stay on the road and are considered more for their historical and architectural aspects rather than for any practical purposes. However, some caravanserais have been restored and turned into interesting, modern hotels such as the Shah Abbas caravanserai in Isfahan.
Notable caravanserais in Iran :
Zin-o-din (Yazd)
Maranjab (Aran o Bidgol)
Robat Sharaf (Mashhad)
Dayr-e Gachin (National Kavir Park)
Moshir-ol-molk (Bushehr)
Qasr-e Bahram (Tehran)
Abbas Abad (Shahrood)
Miandasht (Shahrood)
Robat Karim (Tehran-Saveh road)
Hoz-e Sultan (Qom)
Dodehak (Delijan, Markazi)
Khargoshi (Yazd)
Pasangan (Qom)